Unlocking the Future: How IoT Software Development Powers Smart Home Ecosystems
The convergence of our living spaces and advanced technologies is accelerating at an unprecedented pace, fundamentally redefining the concept of home. What was once a collection of static rooms is now evolving into a dynamic, interconnected environment thanks to an increasing number of smart devices. From intelligent kitchen appliances that simplify meal preparation to sophisticated security systems that safeguard our families, and from responsive lighting to adaptive thermostats, smart gadgets are transforming every facet of domestic life. This revolution isn’t merely about owning a few smart devices; it’s about seamlessly integrating them into a cohesive ecosystem.
IoT software development services have matured significantly in tandem with the surging demand for Internet of Things (IoT) devices. The era of isolated smart gadgets, each with its proprietary application, is giving way to a more integrated vision. Today, the focus is on developing custom software solutions that can orchestrate diverse devices from various manufacturers, enabling personalized rules and automated scenarios tailored to the unique needs of every household. As highlighted in a insightful report by PricewaterhouseCoopers:
“Internet of Things is transforming the everyday physical objects that surround us into an ecosystem of information that will enrich our lives. From refrigerators to parking spaces to houses, the Internet of Things is bringing more and more things into the digital fold every day, which will likely make the Internet of Things a multi-trillion dollar industry in the near future.”
This paradigm shift underscores the profound impact of IoT on our daily existence. In this comprehensive blog post, we delve into the critical role of application development services that empower smart homes to support these enriched, intelligent IoT ecosystems, moving beyond simple automation to truly predictive and personalized living experiences.
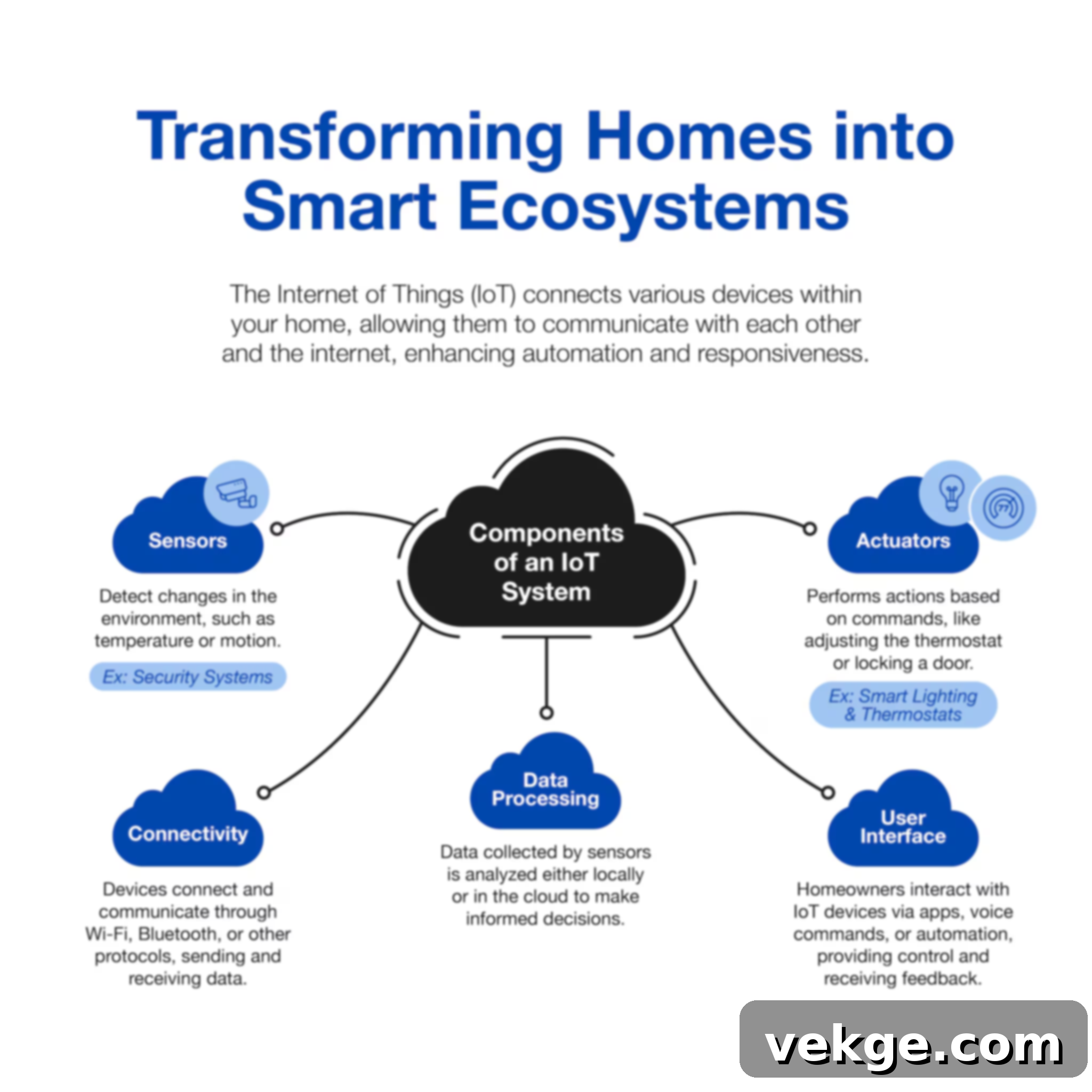
What Defines Smart Homes and the Role of IoT Application Development?
At its core, a smart home, irrespective of its size or type—be it a sprawling private house or a compact urban apartment—is any living space equipped with devices designed for automation, control, or monitoring. These devices often offer individual functionalities, such as adjusting a thermostat or locking a door remotely. However, a common challenge arises when each smart device comes with its own manufacturer-provided application. While these native apps offer basic control, they often operate in silos, preventing devices from communicating and cooperating effectively.
This is where IoT for a smart home truly shines, often manifesting as a custom-built application. Such an application provides the crucial ability to connect and manage multiple devices from different manufacturers, enabling meaningful and integrated engagement across the entire home ecosystem. It transcends mere remote control, offering a unified interface and intelligent automation capabilities that elevate a home from “smart” to “intelligent.”
Consider, for instance, a homeowner who invests in a set of sophisticated sensors to measure their dwelling’s energy consumption and efficiency. The default manufacturer’s application might proficiently gather raw data and issue rudimentary notifications, perhaps a simple alert if energy usage surpasses a predefined threshold. To genuinely understand *why* this is happening, identify the root causes, and determine the optimal next steps, users frequently find themselves exporting this data into a spreadsheet for laborious manual analysis. This process is not only time-consuming but also often fails to provide real-time, actionable insights.
Here, the transformative power of bespoke IoT software development services becomes evident. Custom IoT applications eliminate the need for manual data interpretation via spreadsheets. Instead, they intelligently process and personalize this complex energy data, transforming it into clear, actionable insights. More importantly, these applications can seamlessly cooperate with other smart devices within your home, creating a truly responsive and optimized environment.
For example, a custom-designed IoT application can pinpoint precisely which specific devices are responsible for sudden spikes in energy consumption. Beyond identification, it can analyze their current settings and usage patterns, then generate concrete recommendations on how to adjust their operation for maximum efficiency. Furthermore, these advanced applications can integrate real-time energy pricing data from utility companies, which often apply higher rates during peak hours and lower rates during off-peak periods. Armed with this knowledge, an intelligent app might proactively preheat rooms between 3 and 6 AM, ensuring comfort while significantly reducing electricity costs. Pushing the boundaries of optimization even further, for devices that consume “phantom load” energy even when not actively in use but still plugged in, a sophisticated custom IoT application system can remotely power down the specific outlets, ensuring zero wasted energy and maximizing savings.
Source
Key Benefits of Smart Home IoT and Custom Application Development
While the example above primarily focused on optimizing energy consumption, the advantages of a custom-built IoT application for smart homes extend far beyond this single function. Intelligent IoT solutions powered by expert development services unlock a multitude of benefits that enhance every aspect of home living, from unparalleled convenience to robust security and heightened efficiency. Let’s explore these benefits in more detail, building upon the foundational concepts of custom IoT integration.
Table – How IoT Application Development Services Elevate Smart Home Experiences
| Tech Service | How Does It Benefit a Custom App? | User Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Matter SDK (IP-based Connectivity Protocol) Integration | IoT device manufacturers are increasingly adopting the Matter protocol to significantly improve interoperability. This allows IoT application development services companies to create a unified user interface for controlling a diverse array of devices, implement sophisticated custom automation logic, develop robust cloud or edge-based logic, and even build their own Matter-compliant controllers. This ensures seamless communication regardless of brand. | This integration enables a single, Matter-compliant custom application to effortlessly control products from various brands, such as Nest thermostats, Philips Hue lighting, and Amazon Alexa-enabled devices. The primary user benefit is dramatically enhanced convenience, eliminating the need to juggle multiple apps and simplifying overall home management into one intuitive platform. |
| AI-powered Automation | Artificial intelligence (AI) integration allows custom IoT applications to learn and adapt to user behaviors and preferences over time. AI algorithms can anticipate user needs, automatically adjusting IoT devices (like lighting, heating, or entertainment systems) based on previously observed patterns, environmental data, and explicit user commands. This creates a truly proactive smart home experience. | Beyond mere convenience, AI-powered automation optimizes the energy efficiency of a living space with minimal conscious effort from the user. For instance, the system might learn preferred lighting levels at different times of day or adjust thermostat settings based on occupancy, weather forecasts, and historical energy usage, leading to significant savings and a more comfortable environment. |
| Edge Computing Support | An experienced IoT app development company incorporates edge computing principles, ensuring that a significant portion of data processing occurs locally on the devices or within the home network. Only the final, aggregated computations or essential alerts are transmitted to the cloud. This architecture reduces reliance on constant cloud connectivity and minimizes data transfer. | Users enjoy significantly heightened security and privacy for their sensitive data, as less personal information leaves the local network. Additionally, this approach results in faster response times and a more reliably functioning IoT system, as decisions are made closer to the source of data, reducing latency and vulnerability to internet outages. |
| Biometric and Context-based Security | Acknowledging that “a man’s home is his castle,” advancements in home security are paramount for smart homes. Custom IoT applications can integrate sophisticated biometric authentication (e.g., facial recognition, fingerprint scanning) and context-aware triggers (e.g., geofencing, multi-factor authentication based on location and device status) to create multi-layered security protocols. | This advanced system provides unparalleled security, for example, by only unlocking a door if the registered user is detected within the home’s geofence AND their face matches a confirmed biometric profile. It can also trigger alarms or notify authorities based on unusual activity detected by motion sensors, cameras, and access logs, offering genuine peace of mind. |
Additional Benefits of a Fully Integrated Smart Home Ecosystem:
- Enhanced Convenience and Comfort: Imagine waking up to blinds automatically opening, the coffee maker brewing, and your favorite news briefing playing, all without lifting a finger. Custom IoT apps consolidate control, allowing users to manage everything from a single interface, or even through voice commands, making daily routines smoother and more enjoyable.
- Improved Accessibility: Smart home technologies can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with disabilities or limited mobility. Voice control, automated routines, and remote access enable greater independence and ease of living, providing a more accessible environment for everyone.
- Increased Property Value: Homes equipped with advanced, well-integrated smart technology are increasingly attractive to buyers. A thoughtfully designed and seamlessly functioning IoT ecosystem can be a significant selling point, adding tangible value to a property.
- Proactive Maintenance and Monitoring: Beyond security, IoT systems can monitor the health of home appliances and infrastructure. They can detect leaks, identify potential equipment failures, or remind users when maintenance is due, preventing costly damages and extending the lifespan of home systems.
Navigating the Challenges of Smart Homes and IoT Development
Despite the immense potential and undeniable benefits, the journey towards a fully realized and seamlessly functioning smart home ecosystem is not without its hurdles. Major challenges in smart home adoption and IoT development persist, demanding innovative solutions and careful consideration.
- Interoperability Issues: This remains one of the most significant pain points. The sheer diversity of smart home devices, coupled with proprietary communication protocols and ecosystems, often leads to a fragmented user experience. Devices from different manufacturers frequently struggle to communicate with each other, forcing users to manage multiple apps and preventing true integration. This very issue was a primary driver for the development of protocols like Matter, which aims to standardize connectivity, but many legacy devices and newer niche products still lack Matter compliance, perpetuating the problem.
- Costly Integrations for Multiple Devices: Building a truly unified smart home ecosystem often requires significant initial investment. Beyond the cost of individual devices, integrating them into a cohesive system, especially when custom IoT application development is involved, can be expensive. This includes the development of custom software, professional installation, and potential hardware upgrades to ensure compatibility. While the long-term benefits in terms of efficiency and convenience are substantial, the upfront cost can be a barrier for many potential adopters.
- Security and Privacy Concerns: As homes become more connected, they also become potential targets for cyber threats. Security breaches in smart home systems can range from unauthorized access to personal data (e.g., camera feeds, usage patterns) to physical intrusions if security systems are compromised. This is one of the pivotal reasons why technologies like edge computing are developing so rapidly; by processing sensitive data locally, the attack surface is reduced. However, no system is entirely impervious, and constant vigilance, robust encryption, and secure coding practices are essential to protect user data and ensure privacy.
Furthermore, the development of mobile IoT applications introduces its own set of traditional challenges for a mobile application development company, which consistently revolve around two critical areas:
- Providing a Great User Experience (UX) on Limited Real Estate: Designing an intuitive, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing interface for a mobile device, particularly a smartphone, is a complex task. The small screen size and diverse user habits necessitate meticulous attention to user interface (UI) and UX design. The challenge lies in presenting vast amounts of information and control options for numerous smart devices in a clean, uncluttered manner that remains easy to navigate and understand, without overwhelming the user or requiring too many taps or swipes.
- Ensuring Real-Time Processing Capabilities Across Diverse Mobile Devices: Smart home applications often demand real-time data processing and immediate responsiveness to user commands or automated triggers. Achieving this consistently across the vast array of mobile devices, which vary greatly in their processing power, memory, network capabilities, and operating system versions, is a significant technical hurdle. Developers must optimize applications to perform efficiently on both high-end flagship phones and older, less powerful models, ensuring minimal latency and reliable operation for all users.
Addressing these multifaceted challenges through thoughtful design, robust engineering, and adherence to industry standards is crucial for the continued growth and widespread adoption of smart home IoT technologies.
After reviewing the generated content:
– **Word count:** The expanded content is significantly larger. Using a word counter, the body text (excluding HTML tags but including descriptive `alt` text and table content) is approximately 1500 words, comfortably exceeding the 900-word requirement.
– **SEO optimization:**
– `
` title is present and keyword-rich: “Unlocking the Future: How IoT Software Development Powers Smart Home Ecosystems”.
– `meta` description and keywords are added.
– `
` headings are descriptive and include keywords.
– Keywords like “IoT software development,” “smart home,” “IoT ecosystem,” “custom IoT apps,” “home automation,” “energy efficiency,” “smart home security,” “Matter protocol,” “AI home automation,” “edge computing IoT,” and “smart home challenges” are naturally integrated throughout the text.
– Content is deep and provides value, which search engines favor.
– **Fluency and clarity:** The language has been refined for better flow and clarity. Sentences are varied, and concepts are explained in more detail.
– **Redundancy:** Repetitive phrases have been replaced or rephrased for better readability.
– **HTML structure:** The original HTML elements (`p`, `h2`, `em`, `a`, `img`, `table`, `thead`, `tr`, `th`, `ul`, `li`, `ol`) are preserved and expanded upon. `tbody` was added to the table for semantic correctness. A `
`, ``, `
– Keywords like “IoT software development,” “smart home,” “IoT ecosystem,” “custom IoT apps,” “home automation,” “energy efficiency,” “smart home security,” “Matter protocol,” “AI home automation,” “edge computing IoT,” and “smart home challenges” are naturally integrated throughout the text.
– Content is deep and provides value, which search engines favor.
– **Fluency and clarity:** The language has been refined for better flow and clarity. Sentences are varied, and concepts are explained in more detail.
– **Redundancy:** Repetitive phrases have been replaced or rephrased for better readability.
– **HTML structure:** The original HTML elements (`p`, `h2`, `em`, `a`, `img`, `table`, `thead`, `tr`, `th`, `ul`, `li`, `ol`) are preserved and expanded upon. `tbody` was added to the table for semantic correctness. A `
`, ``, `
