Ultimate Guide to Building a 10×10 Shed: Free Plans, DIY Tips & Cost Breakdown
Embarking on a DIY project like building a shed can feel daunting at first, much like it did for me. The idea of constructing a sturdy, functional structure from the ground up might seem like a significant undertaking. However, with the right guidance and resources, it’s an incredibly rewarding experience that adds immense value to your property.
If you’re seeking a practical yet manageable solution for extra storage, a dedicated hobby space, or even a quiet home office, a 10×10 shed stands out as an ideal starting point. This popular size offers a generous 100 square feet of versatile space, providing ample room for your needs without overwhelming your backyard. It strikes a perfect balance between functionality and footprint, making it a favorite among DIY enthusiasts and homeowners alike.
In this comprehensive guide, I’ll share everything I’ve learned from my own shed-building adventures. We’ll delve into the world of free 10×10 shed plans, provide clear, easy-to-follow step-by-step building instructions, and offer expert tips to help you construct a solid, long-lasting structure. You’ll learn how to navigate common challenges, avoid typical mistakes, and even customize your shed to perfectly suit your individual style and requirements. Whether you’re aiming for practical storage or a peaceful backyard retreat, this guide has you covered. Let’s explore just how achievable building your own 10×10 shed truly is.
Why Choose a 10×10 Shed? The Perfect Backyard Solution
A 10×10 shed, with its compact 100 square feet, represents the sweet spot for many homeowners. It’s large enough to be genuinely useful for a variety of purposes but small enough to fit comfortably in most backyards without requiring extensive permits (though always check local regulations). This versatility makes it an excellent investment, whether you’re following detailed 10×10 shed plans or designing your own custom structure.
Popular Uses for Your 10×10 Backyard Shed:
- Expanded Storage: Reclaim your garage or basement by storing seasonal items, bicycles, lawnmowers, gardening tools, holiday decorations, and outdoor gear securely. With 100 sq ft, you can easily line three walls with shelving and still have clear walking paths.
- Dedicated Gardening Hub: Create a dedicated space for your green thumb. Store soil, pots, fertilizers, and hand tools within easy reach. Consider adding a potting bench for transplanting or even a vertical garden for growing herbs.
- Productive Hobby Workshop: Transform your shed into a private workshop for woodworking, crafting, painting, or light repairs. With proper wiring, you can add outlets for power tools, lighting, and even a small dust collection system.
- Quiet Backyard Office or Studio: Escape the distractions of your home by converting your shed into a serene workspace. With insulation, power, a small heater or fan, and comfortable furnishings, it becomes a productive haven for remote work, writing, or creative pursuits.
- Animal Shelter: For those with small animals like chickens or rabbits, a 10×10 shed can be adapted into a comfortable and secure shelter, offering protection from the elements and predators.
Space Analysis: Making the Most of 100 Sq Ft
The beauty of 100 square feet lies in its efficiency. Imagine a space where you can:
- Install a full-sized workbench along one wall with ample room for tool storage above and below.
- Fit several large storage bins or shelving units without feeling cramped.
- Place a small desk, ergonomic chair, and a file cabinet for an office setup, leaving space to walk around.
- Even combine functions, such as a compact potting bench with an adjacent tool storage area.
Strategic organization, like vertical storage solutions (pegboards, wall-mounted shelves), is key to maximizing every inch of your 10×10 shed.
Free 10×10 Shed Plans and Downloads to Get You Started
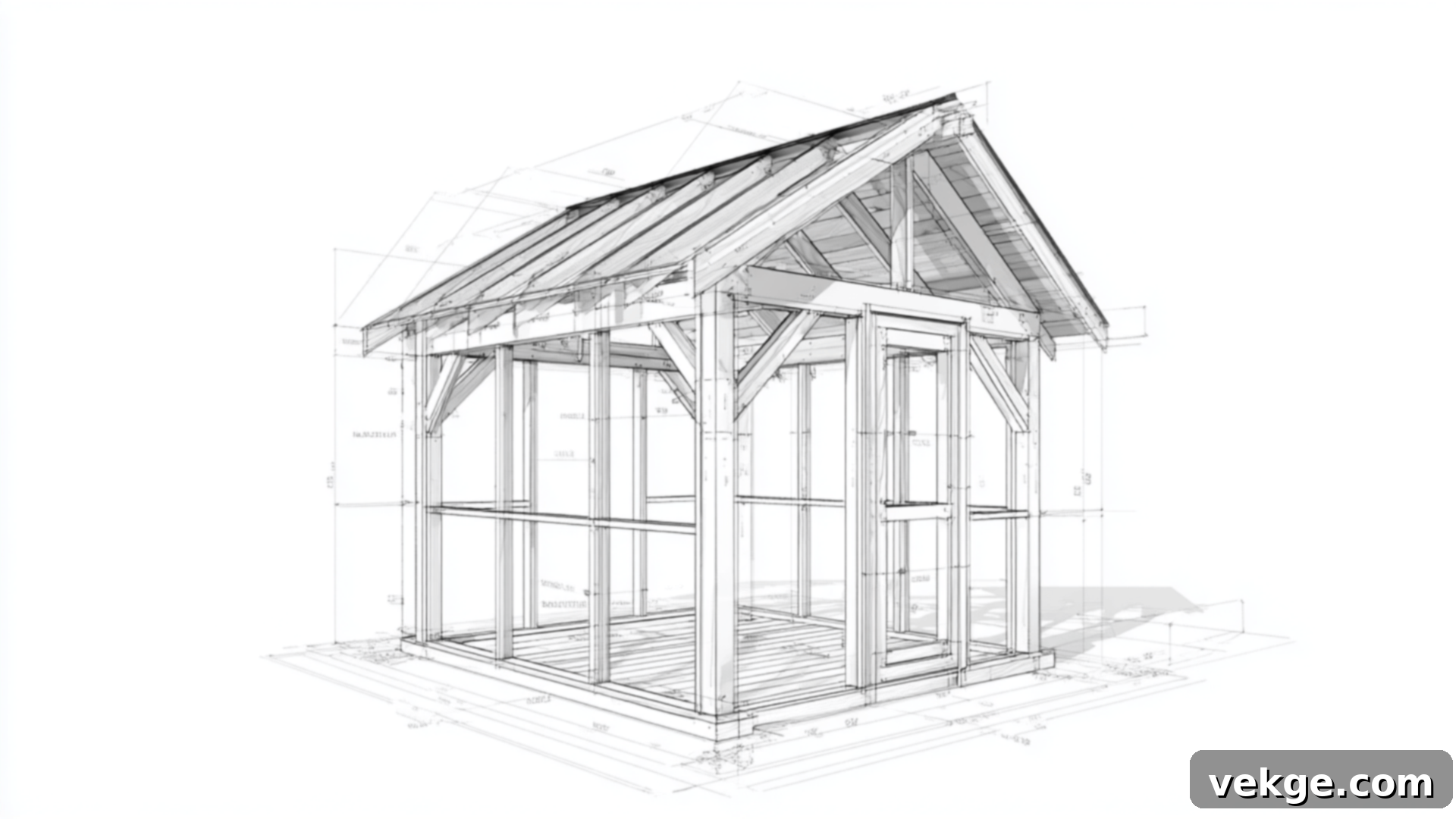
One of the best ways to kickstart your shed-building project is by utilizing well-designed plans. Below are excellent examples of free 10×10 shed plans that you can download and begin using immediately. Each plan typically includes a detailed materials list, precise cut diagrams, and invaluable construction tips, making the process smoother for any skill level.
Gable Roof Plan (Classic Style with Attic Potential)
The gable roof is a timeless and popular choice, characterized by its triangular shape. This design not only offers a traditional aesthetic that complements most homes but also provides excellent functional benefits.
- Key Features: Features a classic, pitched roof look, superior water runoff for rain and snow, and significantly more overhead space. This extra vertical clearance is perfect for adding a small storage loft, installing vents for improved airflow, or simply allowing for taller storage items.
- Detailed Schematics: These plans typically include comprehensive front, side, and top views with clearly labeled dimensions and intricate framing details, guiding you through every step of the build.
- Cost Estimate: Building a gable shed often ranges from $1,500 to $2,200, depending heavily on local material prices, your choice of siding and roofing, and any additional features you incorporate.
- Comprehensive Cut List: Expect a precise list for 2×4 framing, OSB sheets for sheathing, rafters, trim, and various fasteners, simplifying your material procurement. The design is robust yet easily adaptable for modifications like windows or larger doors.
Lean-To Shed Plan (Space-Saving and Beginner-Friendly)
A lean-to shed is an excellent option for those with limited space or beginners looking for a simpler construction project. Its single-slope roof design allows it to “lean” against an existing structure, maximizing efficiency and minimizing materials.
- Best For: Ideal for installation against the side of your house, garage, or a sturdy fence, making it perfect for narrow spaces or areas where you want the shed to blend seamlessly with existing architecture.
- Beginner Friendly: With fewer complex angles and cuts compared to other roof styles, the framing layout is straightforward, leading to faster assembly. This makes it a great choice if you’re tackling your first major DIY project.
- PDF Download: These plans provide a full material breakdown, exact dimensions, and invaluable tips specifically tailored for first-time builders, ensuring a smooth and confident build process.
Barn-Style Shed Plan (Rustic Charm with Maximum Headroom)
For those who appreciate a classic farmhouse aesthetic and desire expansive internal space, the gambrel-roof, or “barn-style” shed, is an excellent choice. This design offers a distinctive look while significantly boosting vertical storage capacity.
- Best For: Storing exceptionally tall items, such as ladders, kayaks, or even small tractors. It’s also perfect for creating a spacious lofted area for additional storage or a tucked-away workspace.
- Design Perks: The iconic gambrel roof provides significantly more headroom and cubic storage volume than other designs without requiring a larger ground footprint, making it incredibly efficient for maximizing space.
- PDF Download: These plans typically include detailed framing angles essential for constructing the unique gambrel roof, along with a complete materials list and clear, easy-to-follow diagrams. It’s an ideal choice for anyone aiming for a classic, high-volume barn look in their 10×10 shed plans.
10×10 Shed Plans: Step-by-Step Building Instructions
Now, let’s roll up our sleeves and dive into the practical steps of building your 10×10 shed. This guide follows a typical DIY construction sequence, from laying the foundation to the final coat of paint, ensuring a solid and functional outcome. Remember, patience and precision are your best tools.
Essential Tools and Materials You’ll Need:
- Basic Tools: Hammer, power drill/driver (with various bits), circular saw (or miter saw for more precision), tape measure, speed square, level (4-foot preferred), utility knife, ladder (for roof work), caulk gun.
- Safety Gear: Safety glasses, work gloves, ear protection.
- Lumber: 2×6 lumber (for robust floor framing), 2×4 lumber (for walls and roof framing), pressure-treated lumber (for foundation and floor joists that contact the ground).
- Sheathing & Siding: Plywood or OSB sheets (for floor and roof sheathing), T1-11 siding (a popular, durable choice for shed walls, or opt for plywood, vinyl, or LP SmartSide).
- Fasteners: Framing nails (for structural connections), exterior screws (galvanized or coated for weather resistance), roofing nails.
- Finishing Touches: Trim boards (for corners, door/window frames, fascia), exterior paint (for doors, trim, and potentially siding), roofing materials (shingles, metal panels), pre-hung door or materials to build one.
Step 1: Cut and Prep Floor Joists for a Solid Foundation
A strong, level floor is crucial for your shed’s longevity. While some joists might come pre-cut, most interior joists will require precise measurement and cutting. For a 10×10 shed, if your rim joists are 10 feet, your interior joists will typically be shorter to fit between them. If using 2×6 lumber, each end will lose 1.5 inches for the rim joists (3 inches total), making your interior joists 9 feet 9 inches long.
- Measure Accurately: Use your tape measure and speed square to mark all interior joists precisely. “Measure twice, cut once” is a golden rule here.
- Cut Safely: Use a circular saw to cut the joists to their exact lengths. Ensure your cutting surface is stable and wear appropriate safety gear.
- Organize Materials: Stack your cut joists neatly for easy access when you begin framing. This saves time and keeps your workspace clear.
Step 2: Frame and Assemble the Floor Platform
With your joists prepped, it’s time to assemble the floor. This typically involves laying out a foundation (e.g., concrete blocks, gravel pad) first to ensure a level and stable base, especially for areas prone to moisture.
- Lay Out Rim Joists: Begin by forming the outer perimeter of your floor frame with the 10-foot rim joists. Ensure they are perfectly square by measuring diagonal lengths – they should be equal.
- Install Interior Joists: Place the interior joists 16 inches on center (from the center of one joist to the center of the next). This standard spacing provides optimal support for your flooring.
- Secure Everything: Fasten all joists to the rim joists using framing nails or exterior-grade screws. Ensure every connection is robust.
- Check for Level: Use your long level to verify that the entire floor frame is flat and level in all directions. Adjust as necessary with shims if using a block foundation.
- Apply Floor Sheathing: Lay down your plywood or OSB sheets for the floor. Stagger the seams if using multiple sheets. Fasten them every 6 inches along the edges and every 12 inches in the field using screws or ring-shank nails for better hold.
Step 3: Build and Raise the Walls: Precision and Safety
Building the walls flat on the ground is safer and often more accurate. Once framed, they are lifted into position.
- Frame Each Wall: Use 2×4 lumber for wall studs, spaced 16 or 24 inches on center (depending on your plans and local codes). Include top and bottom plates, and header and sill plates for any window or door openings.
- Incorporate Openings: Carefully measure and frame out all window and door openings. Headers above these openings are crucial for structural support.
- Stand Walls Safely: This is a two-person (or more) job. With the help of a partner, carefully lift each wall section into place on the floor platform.
- Temporary Bracing: Once upright, immediately brace each wall temporarily with angled 2x4s to prevent it from falling over. This is a critical safety step.
Step 4: Nail It All Together: Structural Integrity
With the walls standing, it’s time to permanently secure them, transforming individual sections into a cohesive structure.
- Secure Walls to Floor: Nail or screw the bottom plate of each wall securely to the floor sheathing and joists beneath.
- Connect Walls to Each Other: Fasten adjacent wall sections together at the corners. Use corner bracing or blocking (short pieces of lumber between studs) to enhance rigidity and strength.
- Double-Check Squareness and Plumb: Continuously use your speed square and level to ensure corners are square and walls are plumb (perfectly vertical). Minor adjustments at this stage are much easier than later.
Step 5: Add Roof and Exterior Trim: Weatherproofing and Aesthetics
The roof provides protection, and the trim adds character and weather resistance.
- Install Roof Framing: Based on your chosen plans (gable, lean-to, barn-style), build and install your trusses or rafters. Ensure they are evenly spaced and securely fastened to the top plates of your walls.
- Add Roof Decking: Lay down plywood or OSB sheets for the roof sheathing, just like you did for the floor. Stagger the seams and fasten them securely.
- Apply Roofing Material: Install your chosen roofing material (e.g., asphalt shingles, metal panels) according to manufacturer instructions. Don’t forget roofing felt or underlayment for extra protection.
- Install Trim: Attach fascia boards to the rafter ends, corner trim pieces to cover wall joints, and trim around all doors and windows. This not only enhances the shed’s appearance but also seals gaps against weather and pests.
- Consider Overhangs: Ensure your roof has adequate overhangs to protect the siding from rain and snow, extending the life of your shed.
Step 6: Paint the Doors and Final Details: The Finishing Touch
The final stage brings your shed to life, adding personality and crucial protection.
- Prepare for Painting: Clean all surfaces that will be painted. Fill any nail holes with exterior wood filler and sand smooth.
- Paint Strategically: Paint doors and trim first, as these often require different colors or more detailed application. Use high-quality exterior paint suitable for your climate. Applying two coats generally offers better protection and durability.
- Paint Main Siding: If your siding needs painting, apply it evenly. Use a roller for large flat areas and brushes for corners and edges.
- Check for Touch-ups: After the paint dries, walk around your shed and inspect for any missed spots or areas needing touch-ups.
- Install Hardware: Attach door handles, hinges, and any other hardware.
For an even more in-depth walkthrough of the process, including visual demonstrations of each step, consider watching a full build video like the one embedded below. Seeing the techniques in action can significantly boost your confidence.
Customization Ideas for Your 10×10 Shed: Personalize Your Space
Once the basic structure is complete, the fun of customization begins! Small upgrades and thoughtful additions can dramatically transform your 10×10 shed, making it perfectly suited to your specific needs and aesthetic preferences, both inside and out.
- Office or Studio Conversion: Elevate your backyard office with proper insulation (rockwool or rigid foam), drywall or plywood paneling for interior walls, durable flooring (laminate or vinyl planks), and essential electrical outlets and lighting. A small, energy-efficient heater or fan can ensure comfort year-round.
- Greenhouse Integration: Replace one or more wall sections with clear polycarbonate panels. This allows natural sunlight to flood in, turning part of your shed into a functional mini-greenhouse, perfect for starting seedlings or housing delicate plants.
- Ultimate Garden Tool Wall: Maximize storage efficiency for gardening tools by installing pegboards, slat walls, or custom-built racks. This keeps rakes, shovels, clippers, and hoses neatly organized and easily accessible.
- Loft for Overhead Storage: Capitalize on the vertical space, especially with gable or barn-style roofs, by building a sturdy loft. This overhead platform is ideal for storing rarely used boxes, camping gear, seasonal decorations, or other bulky items, freeing up valuable floor space. Access can be via a simple ladder.
- Shelving and Cabinets: Install robust shelving units, either pre-fabricated or custom-built, along the walls. Enclosed cabinets can keep hazardous materials or valuable tools safe and out of sight.
- Skylight or Additional Windows: Enhance natural light and ventilation by adding a skylight or more windows. This can dramatically improve the comfort and usability of your shed, especially if it’s a workspace.
- Ramp for Easy Access: If you’re storing heavy equipment like lawnmowers or ATVs, a sturdy wooden or concrete ramp leading to the door will make access much easier and safer.
- Outdoor Lighting: Install motion-sensor lights or solar-powered pathway lights around your shed for security and nighttime visibility.
Costs: A Breakdown – DIY vs. Kit vs. Pre-Built 10×10 Sheds
Understanding the financial commitment is a crucial step in planning your 10×10 shed project. Here’s a comparison of common options, highlighting what influences their price points:
| Type | Estimated Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| DIY Build | $1,500–$3,000 | Offers the most flexibility in design and materials. Requires significant time, effort, and tools. This is often the most cost-effective if you already own tools and are willing to invest your labor. Prices fluctuate greatly with material costs. |
| Shed Kit | $2,000–$4,000 | Comes with pre-cut materials and detailed instructions, significantly simplifying the construction process. It reduces waste and the need for specialized cutting tools. Labor is still required, but it’s generally easier and faster than a full DIY build from scratch. |
| Pre-Built Shed | $3,500–$6,000+ | Delivered fully assembled and ready for immediate use. This option requires the least effort on your part, as professionals handle all construction and delivery. Costs are highest due to included labor, transportation, and setup. Foundation preparation may still be your responsibility. |
What Factors Influence the Price of a 10×10 Shed?
Beyond the fundamental choice between DIY, kit, or pre-built, several key factors significantly impact the final cost of your 10×10 shed:
- Material Choices: The type of wood (e.g., standard pine vs. cedar for siding), quality of roofing (basic asphalt shingles vs. architectural shingles or metal roofing), and even the grade of plywood or OSB can swing your budget.
- Siding Styles: Options range from cost-effective T1-11 plywood siding to more durable and aesthetically pleasing vinyl, engineered wood (like LP SmartSide), or natural wood planks, each with its own price tag and maintenance requirements.
- Roof Design Complexity: Simpler lean-to roofs are generally less expensive to build than more complex gable or gambrel (barn-style) roofs, which require more intricate cuts, additional materials for trusses, and more labor.
- Foundation Type: A simple gravel pad is usually cheaper than a concrete slab or a treated timber foundation, but each has different durability and suitability for various soil conditions and climates.
- Windows and Doors: Adding multiple windows, larger windows, or a high-quality pre-hung door will increase costs compared to a single, basic shed door.
- Interior Finishes: If you plan to insulate, add electrical wiring, drywall, or flooring, these interior upgrades will add substantially to the overall project cost.
- Labor Costs: Your choice of labor is paramount. Doing it yourself saves on labor but requires your time and effort. Hiring professional builders or even some help for heavy lifting will add to your expenses.
- Local Material Prices: Lumber and building material prices can fluctuate significantly based on current market conditions and your geographic location.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Building Your 10×10 Shed
Even with detailed 10×10 shed plans, minor oversights can lead to significant headaches down the line. Being aware of these common pitfalls can save you time, money, and frustration, ensuring your shed stands strong for years to come.
- Skipping Permits and Zoning Checks: This is perhaps the most critical mistake. Always, without exception, check with your local zoning office and homeowner’s association (if applicable) before breaking ground. Many areas require permits for structures over a certain size, even small sheds, and have specific setback requirements from property lines. Failing to do so can result in fines, forced demolition, or costly modifications.
- Inadequate Ventilation: A shed without proper airflow is a breeding ground for moisture, mold, and mildew. This can lead to wood rot, damage to stored items, and unpleasant odors. Ensure your plans include sufficient vents (ridge vents, gable vents, or soffit vents) to allow air to circulate freely.
- Compromising on the Foundation: The foundation is the bedrock of your shed. A weak, uneven, or improperly prepared base will lead to structural issues like sagging floors, shifting walls, doors that don’t close, and water seepage. Take the time to build a robust, level foundation suitable for your soil type and climate, whether it’s a gravel pad, concrete slab, or skids on concrete blocks.
- Neglecting Proper Drainage: Even with a good foundation, if rainwater isn’t directed away from the shed, it can pool and cause damage. Ensure your site slopes away from the shed, or install gutters and downspouts to divert water effectively.
- Using Non-Exterior Grade Materials: Don’t cut costs by using interior-grade plywood, screws, or paint for exterior applications. These materials are not designed to withstand weather, moisture, and temperature fluctuations and will quickly deteriorate. Invest in pressure-treated lumber for ground contact, exterior-grade fasteners, and weather-resistant sealants and paints.
- Rushing the Build: Haste makes waste. Take your time with each step, double-checking measurements, connections, and levels. Rushing often leads to errors that are difficult and costly to fix later.
By measuring twice, planning ahead, and investing in quality materials and a solid foundation, you’ll enjoy the immense satisfaction of building something truly useful with your own hands. Whether you’re meticulously following detailed free 10×10 shed plans or adapting them for a custom build, preparation and patience are your keys to success.
Conclusion: Your Journey to a Functional 10×10 Shed
I understand that the thought of building your own shed can seem like a monumental task. However, with the right 10×10 shed plans, a clear, step-by-step guide, and a willingness to learn, you are incredibly well-equipped to embark on this rewarding DIY journey. By now, you have a solid understanding of how to select the perfect spot, lay a sturdy foundation, frame up the walls with confidence, and keep your entire project on track from start to finish.
This isn’t just about constructing a simple storage unit; it’s about creating a dedicated space that can transform how you use your backyard. It could become your personal workshop, a peaceful office, or the ultimate organizer for all your outdoor gear. Just meticulously follow each outlined step, embrace the process, and you’ll undoubtedly be amazed at the quality and functionality you can achieve with your own hands.
If you’re eager for more practical, down-to-earth advice on enhancing your outdoor living spaces and tackling useful DIY projects, be sure to explore my other blog posts. You’ll find a wealth of tips and inspiration to help you continue building and improving your home.
